-->
Microsoft Visual C 2010 Service Pack 1 Redistributable Package MFC Security Update. A security issue has been identified leading to a vulnerability in MFC applications that are built with Visual Studio 2010 and ship the Microsoft Visual C 2010 Service Pack 1 Redistributable Package.
Connect(); 2016
Volume 31 Number 12
[Visual Studio Development]
By Mikayla Hutchinson; 2016
At Connect(); in November, Microsoft is launching a preview of Visual Studio for Mac. This is an exciting development, evolving the mobile-centric Xamarin Studio IDE into a true mobile-first, cloud-first development tool for .NET and C#, and bringing the Visual Studio development experience to the Mac.
A New Member of the Visual Studio Family
At its heart, Visual Studio for Mac is a macOS counterpart of the Windows version of Visual Studio. If you enjoy the Visual Studio development experience, but need or want to use macOS, you should feel right at home. Its UX is inspired by Visual Studio, yet designed to look and feel like a native citizen of macOS. And like Visual Studio for Windows, it’s complemented by Visual Studio Code for times when you don’t need a full IDE, but want a lightweight yet rich standalone source editor.
Below the surface, Visual Studio for Mac also has a lot in common with its siblings in the Visual Studio family. Its IntelliSense and refactoring use the Roslyn Compiler Platform; its project system and build engine use MSBuild; and its source editor supports TextMate bundles. It uses the same debugger engines for Xamarin and .NET Core apps, and the same designers for Xamarin.iOS and Xamarin.Android.
Compatibility is a key focus of Visual Studio for Mac. Although it’s a new product and doesn’t support all of the Visual Studio project types, for those it does have in common it uses the same MSBuild solution and project format. If you have team members on macOS and Windows, or switch between the two OSes yourself, you can seamlessly share your projects across platforms. There’s no need for any conversion or migration.
Mobile-First, Cloud-First Development
The primary workloads supported by Visual Studio for Mac are native iOS, Android and Mac development via Xamarin, and server development via .NET Core with Azure integration. It gives you all the tools you need to develop the rich, native mobile app experiences that users expect today, and the cloud-based server back ends to power them.
It’s all powered by the C# language you know and love, with the latest C# 7 productivity enhancements. You get the performance of compiled code, the productivity of a modern type-safe language, access to the unique features of each platform, and a rich ecosystem of libraries and tools. You can use your existing experience across the mobile and cloud domains, sharing code between client and server. And with all your projects in one solution, you can take advantage of solution-wide cross-project refactoring and code navigation.
C# isn’t the only language supported in the Visual Studio for Mac preview. For the functional programmers among you, it includes excellent F# support, powered by the same F# compiler used in Visual Studio.
iOS, Android and Mac
With the fragmented mobile market today it’s important to be able to target a wide range of devices. Because it’s based on Xamarin Studio, Visual Studio for Mac has mature support for C#-based iOS, Android and Mac development with the Xamarin Platform. You can take advantage of your existing C# experience and libraries, and share common code across platforms, with full access to the native APIs so you can build a fast, polished native app experience.
For even greater code sharing, you can use the cross-platform Xamarin.Forms UI library, which provides a familiar XAML-based development environment that can target multiple platforms, including iOS, Android, macOS and the Universal Windows Platform (UWP)—though UWP development is currently only supported in Visual Studio—and maps to the native UI on each platform. When you need more control, you can mix and match Xamarin.Forms with direct access to the native toolkits. There’s a huge ecosystem of libraries available for Xamarin via NuGet, too, including platform-specific libraries, bindings to native code and portable .NET Standard libraries.
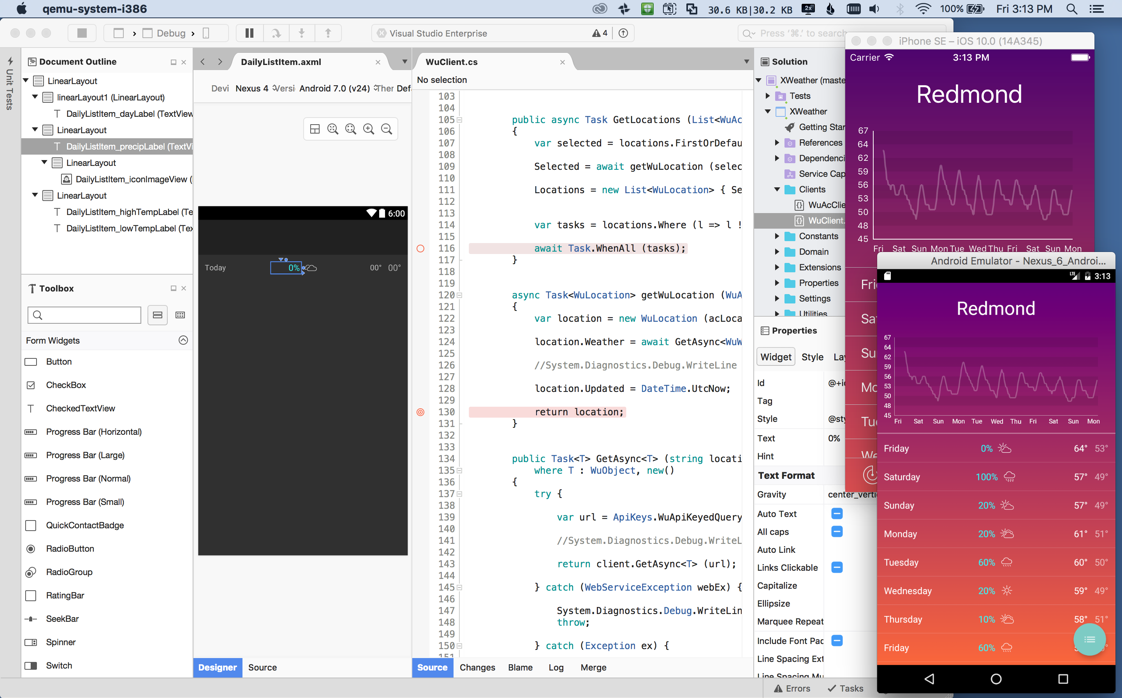
Like Visual Studio, Visual Studio for Mac has drag-and-drop designers for iOS and Android development that let you rapidly assemble and fine-tune your UI. For Xamarin.Forms, it has rich XAML IntelliSense and a side-by-side live preview, as Figure 1 shows. Both the designer and the live preview use a simulator to render your app exactly how it will appear on the device, and this even works for your custom controls.
Figure 1 The Xamarin.Forms XAML Live Preview
Cutting-Edge Cloud
Almost every mobile app is backed by a service, and Visual Studio for Mac makes it easy to develop your app’s service with its support for the latest ASP.NET Core Web development platform. ASP.NET Core runs on .NET Core, the latest evolution of the .NET Framework and runtime. It’s been tuned for blazingly fast performance, factored for small install sizes, and reimagined to run on Linux and macOS, as well as Windows.
.NET Core gives you a huge degree of flexibility in how and where you develop and deploy your server application, whether in your own datacenter or on a cloud platform such as Microsoft Azure. Because both .NET Core and Xamarin Platform are open source, you won’t have to worry about vendor lock-in.
The Visual Studio for Mac support for .NET Core projects also allows you to write .NET Standard libraries, the new way to share code across .NET platforms going forward. .NET Standard libraries replace Portable Class Libraries (PCLs) and offer a much broader API surface area. Because .NET Core and Xamarin Platform are .NET Standard-compliant, they’re a great way to share code, both within your solution and via the NuGet Package Manager.
A Familiar Workspace
The Visual Studio for Mac workspace should be familiar to existing Visual Studio developers. When you first open it, you see a Welcome Page with a list of recently opened solutions, a feed of developer news and other information to help you get started.
To create a new solution, go to the File menu and select New Project, and you’ll see the workspace containing your new solution. As you can see in Figure 2, there’s a central tabbed source editor with a number of other docked windows or “pads” around it, such as Solution, Output, Properties, Document Outline and Toolbox. Like Visual Studio, this layout is highly customizable and switches automatically, depending on whether you’re coding, debugging or using the drag-and-drop designer.
Figure 2 The Visual Studio for Mac Workspace
The toolbar is familiar, too, but has a few notable differences:
On the left is the Run button, a dropdown to select the Active Configuration, as well as dropdowns to select the Run Configuration and Target Device. For cross-platform mobile development, it’s important to be able to easily switch the device or simulator on which you’re testing or debugging your app. The Run Configuration is like the startup project in Visual Studio, except that in addition to switching which project runs, you can also create custom-named sets of run options.
In the center of the toolbar is a notification area, which shows messages about various operations, such as building or restoring NuGet packages. When there’s a running operation, a cancel button shows up in the notification area. This is also where notifications about software updates are displayed. You can click on some notifications, such as build errors, and they’ll bring up a pad with more information.
At the right of the toolbar is the global search. In addition to helping you find things like commands and files in your solution, its camelCase filtering system makes it an excellent way to quickly activate commands, or jump to files or types in your solution. It can even kick off a Find in Files search in your solution, or open the NuGet Package Manager to search for a package.
The Solution pad works much the same as the Solution Explorer in Visual Studio, letting you explore and manage the structure of your solution, your project and the files in it. The context menu gives you a range of context-specific commands on the items in the solution tree, such as adding or removing files from projects, editing project references, opening Terminal windows in folders, and building or debugging specific projects.
The Errors pad shows any build warnings and errors, and is also where you can find the build log output in a split view. Unlike Visual Studio, there isn’t a single unified pad for all kinds of output. For example, an Application Output pad shows the output from your app when you run or debug it, and logs from NuGet operations are shown in a NuGet Console pad. The Properties pad contextually shows properties of whatever is currently focused and selected, and can be used to view and change the build action of files in the solution pad.
In the center is the heart of the IDE, the source editor, which has all the features you’d expect from a member of the Visual Studio family. Figure 3 shows C# IntelliSense and syntax highlighting in a .NET Core project. There’s also code folding, live underlining of errors and suggestions as you type, configurable automatic formatting, code navigation commands and an array of powerful refactoring tools.
Figure 3 IntelliSense in a .NET Core Project
Not all of the editor’s functionality is enabled by default. You can tweak the Visual Studio for Mac settings in the Preferences dialog, which is accessible from its Mac application menu. This is equivalent to the Options dialog in the Visual Studio Tools menu, and contains plenty of options to help you customize the IDE to work the way you want.
Unit testing is supported using NUnit, and other test runners can be plugged in via extensions. The tests discovered in your assembly are shown in a Unit Tests pad that can be accessed from the View | Pads menu. There’s also git version control integrated right into the source editor, with a row of tabs along the bottom of the editor to access the current file’s log, diff and blame view.
If you’d like to get up to speed quickly with some more tips and tricks, I encourage you to watch my “Become a Xamarin Studio Expert” session from Xamarin Evolve 2016 (xmn.io/xs-expert) as its content applies directly to Visual Studio for Mac.
Open Source Core
Like Xamarin Studio, Visual Studio for Mac is based on the open source MonoDevelop IDE, which is actively developed by Microsoft. It’s written entirely in C#, and has a rich extensibility model that you can use to add functionality ranging from simple editor commands to entirely new languages and project types. Even core features such as C# editing, Xamarin.iOS, Xamarin.Android and ASP.NET Core are implemented as extensions.
Like Visual Studio and Visual Studio Code, the C# support in Visual Studio for Mac is powered by the open source Roslyn Compiler Platform. You get the exact same IntelliSense experience you’re familiar with from Visual Studio, as well as support for in-editor live Analyzers and Code Fixes. Visual Studio for Mac even includes the Refactoring Essentials collection of Analyzers and Code Fixes by default.
Visual Studio for Mac supports editing a wide range of languages though the use of TextMate bundles, which provide syntax highlighting and simple IntelliSense. It includes a number of open source TextMate bundles from Visual Studio Code.
Creating an ASP.NET Core App
To show you how easy it is to get up to speed with Visual Studio for Mac, I’m going to walk though creating a simple ASP.NET Core back end. It’s for a hypothetical “Shared To-do List” mobile app, which allows multiple users to add items, and all users see the items that any of them post.
Please note that I’m writing this article using a pre-release version of Visual Studio for Mac, and some details of the UI may change in the release. However, the approaches and concepts discussed in this article will still apply.
After installing and opening Visual Studio for Mac, I start by clicking on the New Solution button on the welcome page, which opens the New Project dialog. I navigate into the Cloud section, choose the ASP.NET Core Web Application template, and click Next, then choose the Web API template. The Web API template creates a RESTful Web service which is perfect for a mobile back end, though you can add views to the project later to create a Web front end.
Finally, I name my project HelloVSMac and click Create. Visual Studio for Mac creates the projects using the dotnet templating engine, opens it and starts restoring the NuGet packages on which it depends. If you open the project file in the editor using the Tools | Edit File context menu on the project in the solution pad, you can see that it’s a minimalistic MSBuild-based project file that’s intended to be easy to understand. If you edit it directly and save it, the IDE will automatically reload your modified version.
Looking at the project in the solution pad, the key items are:
Packages: Your project’s NuGet package dependencies. ASP.NET Core, the .NET Core framework and the MSBuild targets that build the project are all installed via NuGet packages.
Microsoft Developer Downloads
Program.cs: The entry point of your Web app. ASP.NET Core apps are programs, so there’s a Main method entry point that creates, builds and runs the WebHost at the heart of your app.
Startup.cs: Which defines a Startup class that was passed to the WebHost. This class contains your application’s initialization methods.
appsettings.json: Your app’s configuration settings. This is the ASP.NET Core equivalent of the ASP.NET web.config.
For the purposes of this walk-through, I’ll leave these all as is, and look at the ValuesController.cs file in the Views folder. This contains a ValuesController class registered on the [Route('api/[controller]')] route. The [controller] is a placeholder for the class name, so this is really the api/values route.
I’ll start by defining a very simple ToDoItem class and a ToDoList storage class. ToDoList is static so it can be shared among requests. In a real app you’d use a database for this, but it will do for now. I also rename the controller class to ToDoController (which makes the route api/todo), connect the Get and Post methods to the store, and clear out the other unused controller methods. The result can be seen in Figure 4.
Figure 4 The Controller and Its Simple Shared To-Do List Storage
This is now a complete, but very small, RESTful Web service. Let’s try it out.
I place a breakpoint in the Post method, and start debugging the app. The Output pad starts to show the output from the ASP.NET Core built-in kestrel Web server as the app starts up, by default on port 5000, but it won’t do anything else until it receives a request. You can open your Web browser and check 127.0.0.1:5000/api/todo, but it’ll just be an empty array.
Figure 5 Debugging a .NET Core Project
Because there isn’t a mobile client for this service yet, it’s time to open the macOS Terminal app and use curl to send a POST request to the app:
This triggers the breakpoint in the debugger. You can inspect the value that has automatically been parsed from the JSON body of the request and converted into the ToDoItem object. You can see that Visual Studio for Mac automatically entered the debugging layout, and has all the debugger pads you’d expect: Stack, Locals, Threads, Breakpoints and so on.
Now, go back to the terminal and use curl to access the Get method, and you’ll see the JSON array containing the item that was added:
The next step is to build the mobile app, but I’ll let you explore that yourself. For more in-depth information on ASP.NET Core, I recommend checking out asp.net/get-started, and if you’d like to learn more about Xamarin development, there’s plenty of great material at developer.xamarin.com. Although there isn’t much documentation on Visual Studio for Mac yet, the Xamarin Studio documentation applies directly in most cases, and Visual Studio documentation is often applicable, too.
Wrapping Up
I hope this brief overview has whetted your appetite to try Visual Studio for Mac and make it your macOS IDE of choice for cloud and mobile development! If you have a Mac I encourage you to download the preview from VisualStudio.com, give it a spin, and let us know how you like it. We’re excited to hear your feedback to help guide it through the preview and beyond.
Mikayla Hutchinsonis a senior program manager on Xamarin Platform at Microsoft. Previously she developed the mobile and Web tooling for Xamarin Studio and was a core developer on MonoDevelop. You can follow her on Twitter: @mjhutchinson.
Thanks to the following Microsoft technical experts for reviewing this article: Larry O’Brien and Lluis Sanchez
Larry O'Brien works in the Xamarin documentation group at Microsoft. He has long been active in the software development publication field as both author and editor.
Microsoft Developer Studio Fortran
-->Visual Studio for Mac has debuggers with support for .Net Core, .NET Framework, Unity, and Xamarin applications.
Visual Studio for Mac uses the Mono Soft Debugger, which is implemented into the Mono runtime, allowing Visual Studio for Mac to debug managed code across all platforms.
The Debugger
Visual Studio for Mac uses the Mono Soft Debugger to debug managed (C# or F#) code in all Xamarin applications. The Mono Soft debugger is different from regular debuggers in that it is a cooperative debugger that is built into the Mono runtime; the generated code and Mono runtime cooperate with the IDE to provide a debugging experience. The Mono runtime exposes the debugging functionality through a wire protocol, which you can read more about in the Mono documentation.
Hard debuggers, such as LLDB or GDB, control a program without the knowledge or cooperation from the debugged program, but can still be useful when debugging Xamarin applications in the event that you need to debug native iOS or Android code.
For .NET Core and ASP.NET Core applications, Visual Studio for Mac uses the .NET Core debugger. This debugger is also a cooperative debugger and works with the .NET runtime.
Using the debugger
To start debugging any application, always ensure that the configuration is set to Debug. The debug configuration provides a helpful set of tools to support debugging, such as breakpoints, using data visualizers, and viewing the call stack:
Setting a breakpoint
Microsoft Developer
To set a breakpoint in your IDE, click on the margin area of your editor, next to the line number of the code where you wish to break:
You can view all the breakpoints that have been set in your code by going to the Breakpoints pad:
Start debugging
To start debugging, select the target browser, device, or simulator/emulator:
Then deploy your application by pressing the Play button, or Cmd + return. When you hit a breakpoint, the code will be highlighted yellow:
Debugging tools, such as the one used to inspect the values of objects, can be used at this point to get more information about what is happening in your code:
Conditional breakpoints
You can also set rules dictating the circumstances under which a breakpoint should occur, this is known as adding a conditional breakpoint. To set a conditional breakpoint, access the Breakpoint Properties window, which can be done in two ways:
- To add a new conditional breakpoint, right-click on the editor margin, to the left of the line number for the code you wish to set a breakpoint on, and select New Breakpoint:
- To add a condition to an existing breakpoint, right-click on the breakpoint and select Breakpoint Properties, or, in the Breakpoints Pad, select the Edit Breakpoint button illustrated below:
Microsoft Developer Studio Express
You can then enter the condition under which you want the breakpoint to occur:
Stepping through code
Microsoft Developer Studio For Mac Windows 10
When a breakpoint has been reached, the Debug tools enable you to get control over the program's execution. Visual Studio for Mac will display four buttons, allowing you to run and step through the code. In Visual Studio for Mac, they will look like the following:
Here are the four buttons:
- Play - This will begin executing the code, until the next breakpoint.
- Step Over - This will execute the next line of code. If the next line is a function call, Step Over will execute the function, and will stop at the next line of code after the function.
- Step Into - This will also execute the next line of code. If the next line is a function call, Step Into will stop at the first line of the function, allowing you to continue line-by-line debugging of the function. If the next line is not a function, it will behave the same as Step Over.
- Step Out - This will return to the line where the current function was called.
Debugging Mono's class libraries
Xamarin products ship with the source code for Mono's class libraries, and you can use this to single step from the debugger to inspect how things are working under the hood.
Since this feature consumes more memory during debugging, it is turned off by default.
To enable this feature, browse to Visual Studio for Mac > Preferences > Debugger and ensure that the 'Step into external code' option is selected, as illustrated below: